DRI Calculator for Healthcare Professionals Use this tool to calculate daily nutrient recommendations for dietary planning based on the Dietary Reference Intakes (DRIs) These represent the most current scientific knowledge on nutrient needs, developed by the National Academy of Science's Institute of MedicineOn what are the best values to use for our controlled populations To date, I am awaiting clarification from the Ameri can Dietetic Association as to how best interpret and use the DRI's for menu approvals for our populations To put this in perspective Our correctional menus are approved by a registered and/ or licensed dietitian;Manganese, or other nutrients not yet evaluated via the DRI process As retinol activity equivalents (RAEs) 1 RAE = 1 a mg retinol, 12 g βcarotene, 24 αcarotene, or 24 mg βcryptoxanthin The RAE for dietary provitamin A carotenoids is twofold greater than retinol equivalents (RE), whereas the RAE for preformed vitamin A is the same as RE

4 General Guidance For Users Of Dris Session 3 The Development Of Dris 1994 04 Lessons Learned And New Challenges Workshop Summary The National Academies Press
Dri values usda
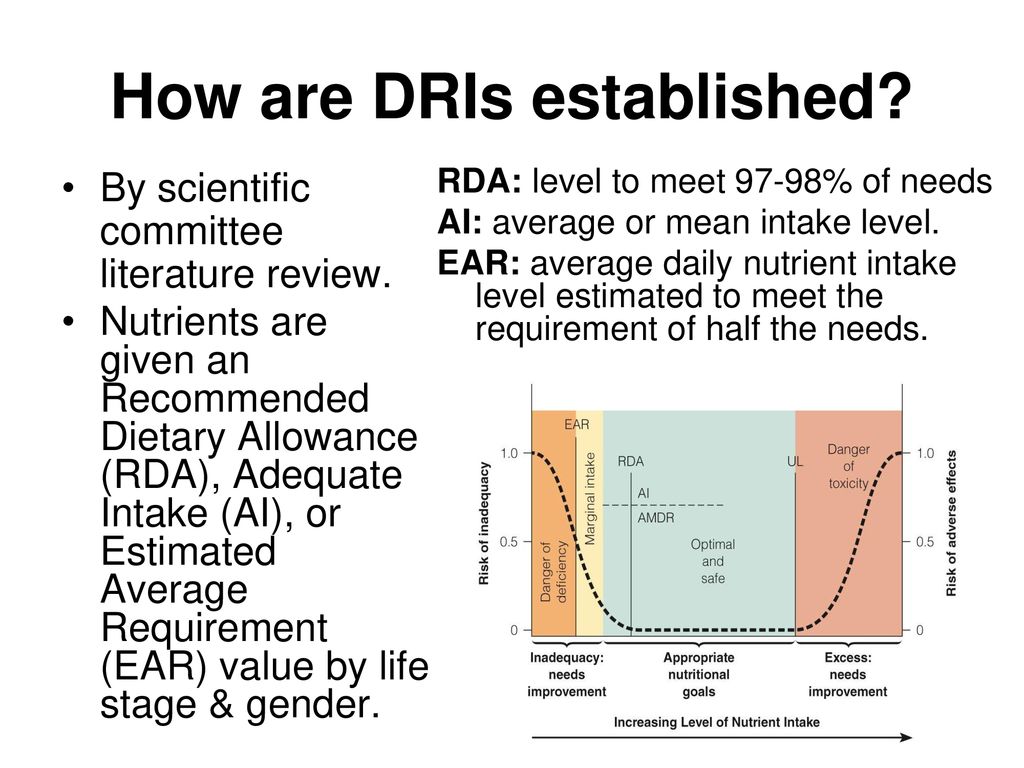
Dri values usda-DRI is the general term for a set of reference values used to plan and assess nutrient intakes of healthy people These values, which vary by age and sex, include Recommended Dietary Allowance (RDA) Average daily level of intake sufficient to meet the nutrient requirements of nearly all (97–98%) healthy individuals; · DRI is the general term for a set of reference values used for planning and assessing nutrient intakes of healthy people These values, The US Department of Agriculture's (USDA's) FoodData Central lists the nutrient content of many foods and provides a comprehensive list of foods containing vitamin C arranged by nutrient content and by food name Dietary supplements




2a Dietary And Nutritional Guidelines 5 Oer Lecture Ideas Holding Site
USDA's Interactive DRI Tool for Health Care Professionals On August 15, 19, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) issued guidance providing stepbystep instruction on converting previous units of measure for folate, niacin, vitamin A, vitamin D, and vitamin E to the new units required on the updated Nutrition Facts and Supplement Facts labels · DRI Activities Update — March The National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine (NASEM) has developed an educational webpage, Expansion of the Dietary Reference Intake Model Learning from Sodium and Potassium, to followup on the 19 Dietary Reference Intakes for Sodium and Potassium reportOften used to plan nutritionally adequate diets for individuals
The DRIs are a set of reference values developed jointly for the United States and Canada by the National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine The DRI model, which was developed in recognition of the need for a safe and adequate range of intakes, had intended that evidence on chronic disease risk be incorporated in the process How ever, relationships between nutrientThis practice is reflective of most gov · The percentages of individuals meeting the Dietary Reference Intakes 1 (DRI) are based on day1 nutrient intakes from the CSFII and DRI values established during the period from the mid 1990's to 02 Pyramid Servings groups (fruit, grain, vegetable, dairy, and meat) estimates are for individuals 2 years old and over who meet the minimum daily servings recommendations
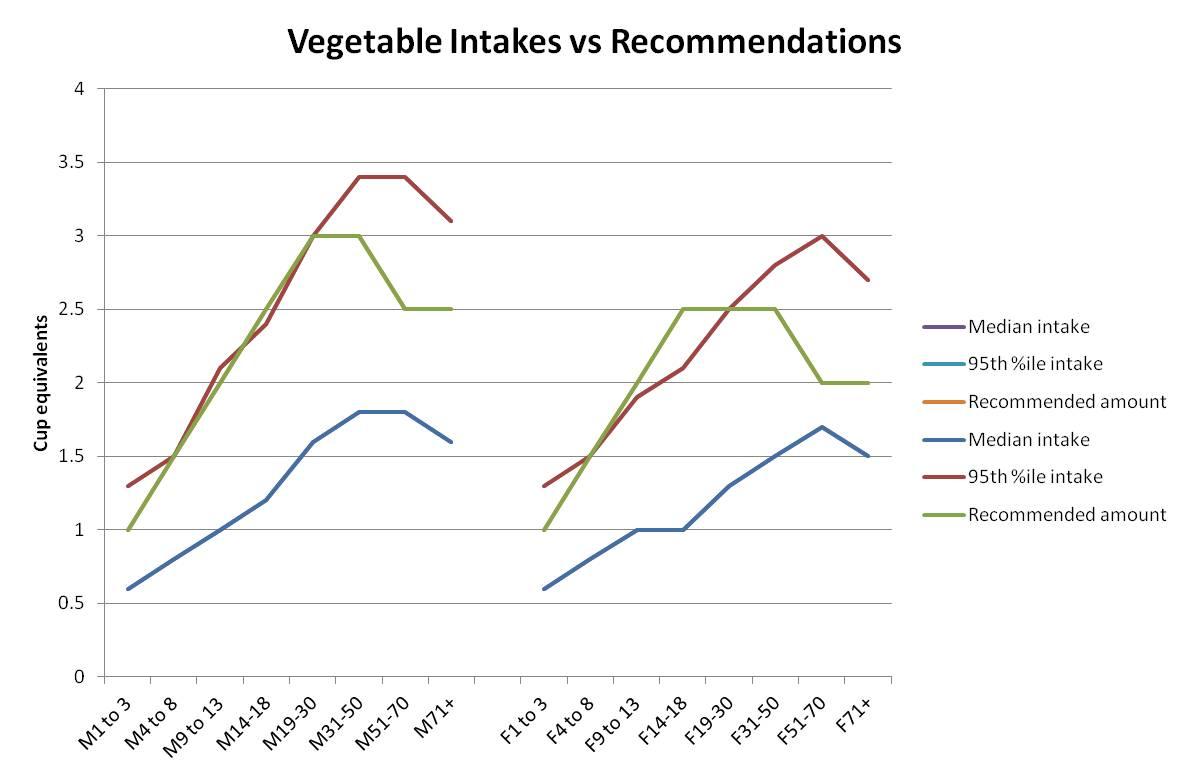
The amount of fruit you need to eat depends on your age, sex, height, weight, and level of physical activity For women, the amount can also depend on whether you are pregnant or breastfeeding Find the right amount for you by getting your MyPlate Plan For general recommendations by age, see the table belowThe DRI values and paradigm replace the former Recommended Dietary Allowances (RDAs) for the United States and Recommended Nutrient Intakes (RNIs) for Canada In the past, RDAs and RNIs were the primary values available to US and Canadian health professionals for planning and assessing the diets of individuals and groups The DRIs represent a more complete set of · The DRI and daily value both provide information about nutrients, but the DRI establishes the guidelines for how much of each nutrient you need, while the daily value tells you how much of the nutrients you're actually getting from the foods you eat The scope of information they provide is also different DRI includes four groups of detailed information, while the daily



Appendix E 3 1 Health Gov




Chapter 2 Nutrition Tools Standards And Guidelines Nutrition Concepts Controversies 12e Sizer Whitney Slideshow And Powerpoint Viewer Learning Objectives Explain How Rda Ai Dv And
Home Dietary Guidelines for AmericansRead chapter 10 Protein and Amino Acids Responding to the expansion of scientific knowledge about the roles of nutrients in human health, the Institute oThe research is related to DRI values that were difficult to meet as a part of eating plans that are consistent with the Dietary Guidelines for Americans 05 (DHHS/USDA, 05) Background information of the derivation of specific Estimated Average Requirements (EARs), RDAs, or AIs is provided to help clarify the continuing research needs Carbohydrates Recommended Dietary




Diet Analysis Part 3 Nutrient Analysis




Chapter 2 Nutrition Tools Standards And Guidelines Nutrition Concepts Controversies 12e Sizer Whitney Slideshow And Powerpoint Viewer Learning Objectives Explain How Rda Ai Dv And
This table (taken from the DRI reports, see wwwnapedu) presents Recommended Dietary Allowances (RDAs) in bold type and Adequate Intakes (AIs)For example, the DV for sodium has been updated from 2,400mg to 2,300mg That means that a packaged food with 1,060mg of sodium in one serving (previously 44% DV) now has · The percentages of individuals meeting the Dietary Reference Intakes 1 (DRI) are based on day1 nutrient intakes from the CSFII and DRI values established during the period from the mid 1990's to 02 Pyramid Servings groups (fruit, grain, vegetable, dairy, and meat) estimates are for individuals 2 years old and over who meet the minimum daily servings recommendations



What Is A Dietary Reference Intake



Report An Issue Cronometer
· With this app, the USDA's Food and Nutrition Information Center • puts the National Academy of Sciences' Institute of Medicine's DRI recommendations at the fingertips of health care practitioners, including Registered Dietitians (RDs), doctors, nurse practitioners and others who can help consumers interpret and use these DRI values to guide healthy dietary behaviorsDRI Calculator for Healthcare Professionals This tool will calculate daily nutrient recommendations based on the Dietary Reference Intakes (DRIs) established by the Health and Medicine Division of the National Academies of Sciences, Engineering and Medicine The data represents the most current scientific knowledge on nutrient needs however individual requirements may be higher or lower than DRIE DRI Values for Indispensable Amino Acids by Life Stage and Gender Group 459–465;




Foods And Nutrition 1021 Chapter Notes




The Dietary Guidelines For Americans Were Developed Chegg Com
This is a fact sheet intended for health professionals For a readerfriendly overview of Magnesium, see our consumer fact sheet on Magnesium Introduction Magnesium, an abundant mineral in the body, is naturally present in many foods, added to other food products, available as a dietary supplement, and present in some medicines (such as antacids and laxatives)4 Copper values for mil kare given in mg and DRI are given in µg, conversion is 1 mg = 1000 µg 5 Potassium and sodium values for milk are given in mg and DRI are given in g, conversion is 1 g = 1000 mg Table 4 Daily reference intake (DRI) values for vitamins and minerals Compiled from USDA RDI tablesIncludes five distinct data types that provide information on food and nutrient profiles Foundation Foods, Food and Nutrient Database for Dietary Studies 1718 (FNDDS 1718), National Nutrient Database for Standard Reference Legacy Release (SR Legacy), USDA Global Branded Food Products Database (Branded Foods), and Experimental Foods Each of these data types has a




Usda Food Pattern For A 00 Calorie Diet From 1 Download Table



Appendix E 3 1 Health Gov
The DRIs are a common set of reference values for a healthy population based on the relationships between nutrient intakes and health or the prevention of disease DRI is a generic term for a set of nutrient reference values that include the EAR, the RDA, the AI and the ULOften used to plan nutritionally adequate diets for individualsThe Dietary Reference Intakes (DRI) provide reference values for vitamins, minerals and other nutrients that 1) indicate daily intake amounts that meet the needs of most healthy people, and 2) set intake levels not to exceed to avoid harm These reference values provide an important source of evidence for the Dietary Guidelines by helping us understand if the population is meeting or




2a Dietary And Nutritional Guidelines 5 Oer Lecture Ideas Holding Site




Nutrition Facts Label Wikipedia
Dietary Reference Intakes (DRI) The Dietary Reference Intakes (DRI) include two sets of values that serve as goals for nutrient intake—Recommended Dietary Allowances (RDA) and Adequate Intakes (AI) The RDA reflect the average daily amount of a nutrient considered adequate to meet the needs of most healthy people If there is insufficient evidence to determine an RDA, an AI is set · The percentages of individuals meeting the Dietary Reference Intakes 1 (DRI) are based on day1 nutrient intakes from the CSFII and DRI values established during the period from the mid 1990's to 02 Pyramid Servings groups (fruit, grain, vegetable, dairy, and meat) estimates are for individuals 2 years old and over who meet the minimum daily servings recommendations · These values, which vary by age and sex, include Recommended Dietary Allowance (RDA) Average daily level of intake sufficient to meet the nutrient requirements of nearly all (97%–98%) healthy individuals;




Test Bank For Nutrition Concepts And Controversies 14th Edition By Sizer Ibsn By Hales86 Issuu




Test Bank For Nutrition And You 4th Edition By Blake Ibsn By Oginz Issuu
Reference values (Medicine) DNLM 1 Nutrition 2 Diet 3 Reference Values I Institute of Medicine (US) Panel on Macronutrients II Institute of Medicine (US) Standing Committee on the Scientific Evaluation of Dietary Reference Intakes QP141D529 05 6132—dc22 · The Dietary Reference Intake is a system of nutrition recommendations from the National Academy of Medicine (NAM) of the National Academies It was introduced in 1997 in order to broaden the existing guidelines known as Recommended Dietary Allowances The DRI values differ from those used in nutrition labeling on food and dietary supplement products in the US and Canada, which uses Reference Daily Intakes and Daily Values · Following a request from the European Commission, the EFSA Panel on Nutrition, Novel Foods and Food Allergens (NDA) derived dietary reference values (DRVs) for sodium Evidence from balance studies on sodium and on the relationship between sodium intake and health outcomes, in particular cardiovascular disease (CVD)related endpoints and bone health, was




Valley Farms Posts Facebook




National Agricultural Library
H Standard Deviation of Requirements for Nutrients with an EAR · The percentages of individuals meeting the Dietary Reference Intakes 1 (DRI) are based on day1 nutrient intakes from the CSFII and DRI values established during the period from the mid 1990's to 02 Pyramid Servings groups (fruit, grain, vegetable, dairy, and meat) estimates are for individuals 2 years old and over who meet the minimum daily servings recommendations · The percentages of individuals meeting the Dietary Reference Intakes 1 (DRI) are based on day1 nutrient intakes from the CSFII and DRI values established during the period from the mid 1990's to 02 Pyramid Servings groups (fruit, grain, vegetable, dairy, and meat) estimates are for individuals 2 years old and over who meet the minimum daily servings recommendations
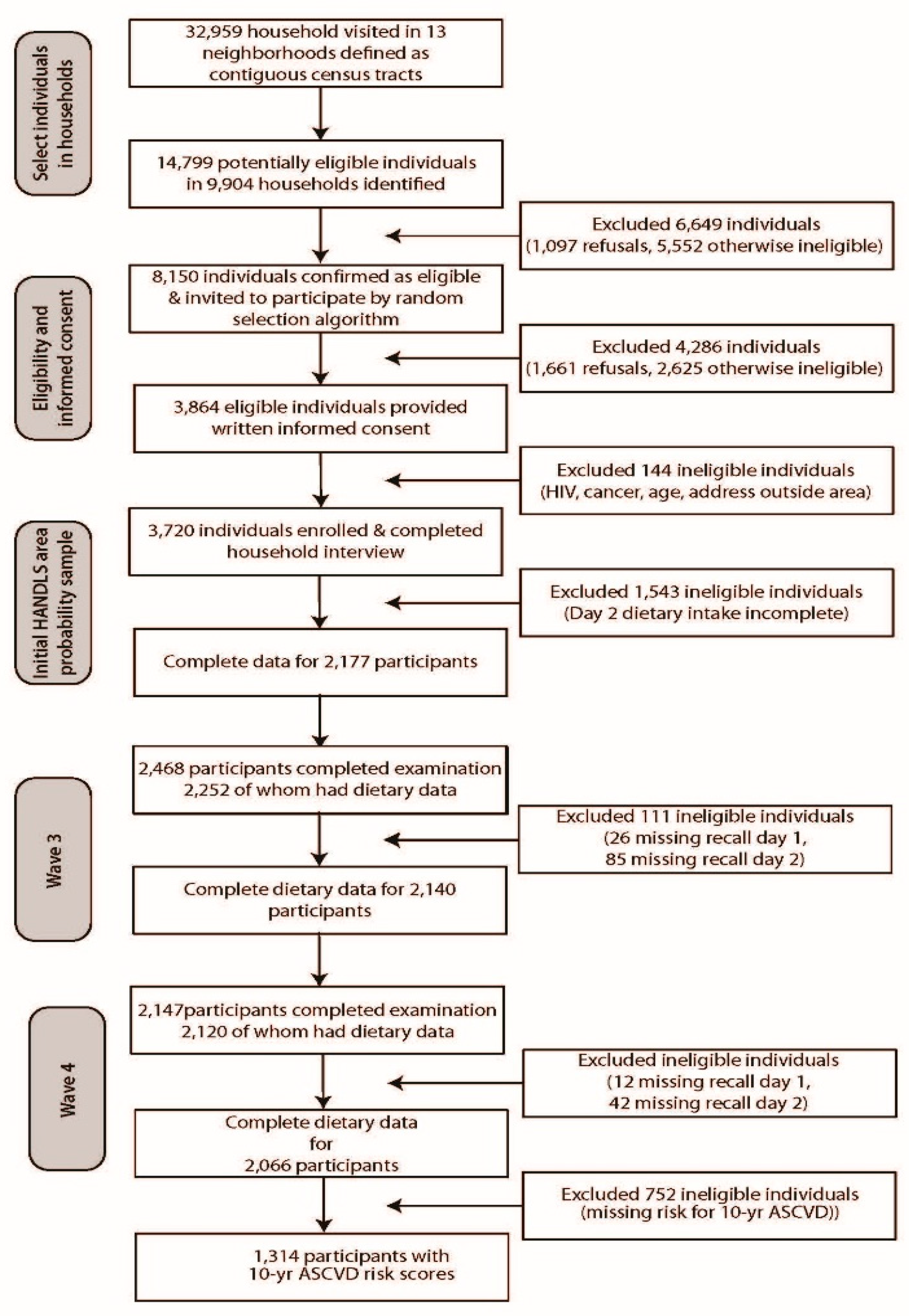



Nutrients Free Full Text Aspects Of Dietary Diversity Differ In Their Association With Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Risk In A Racially Diverse Us Adult Population Html
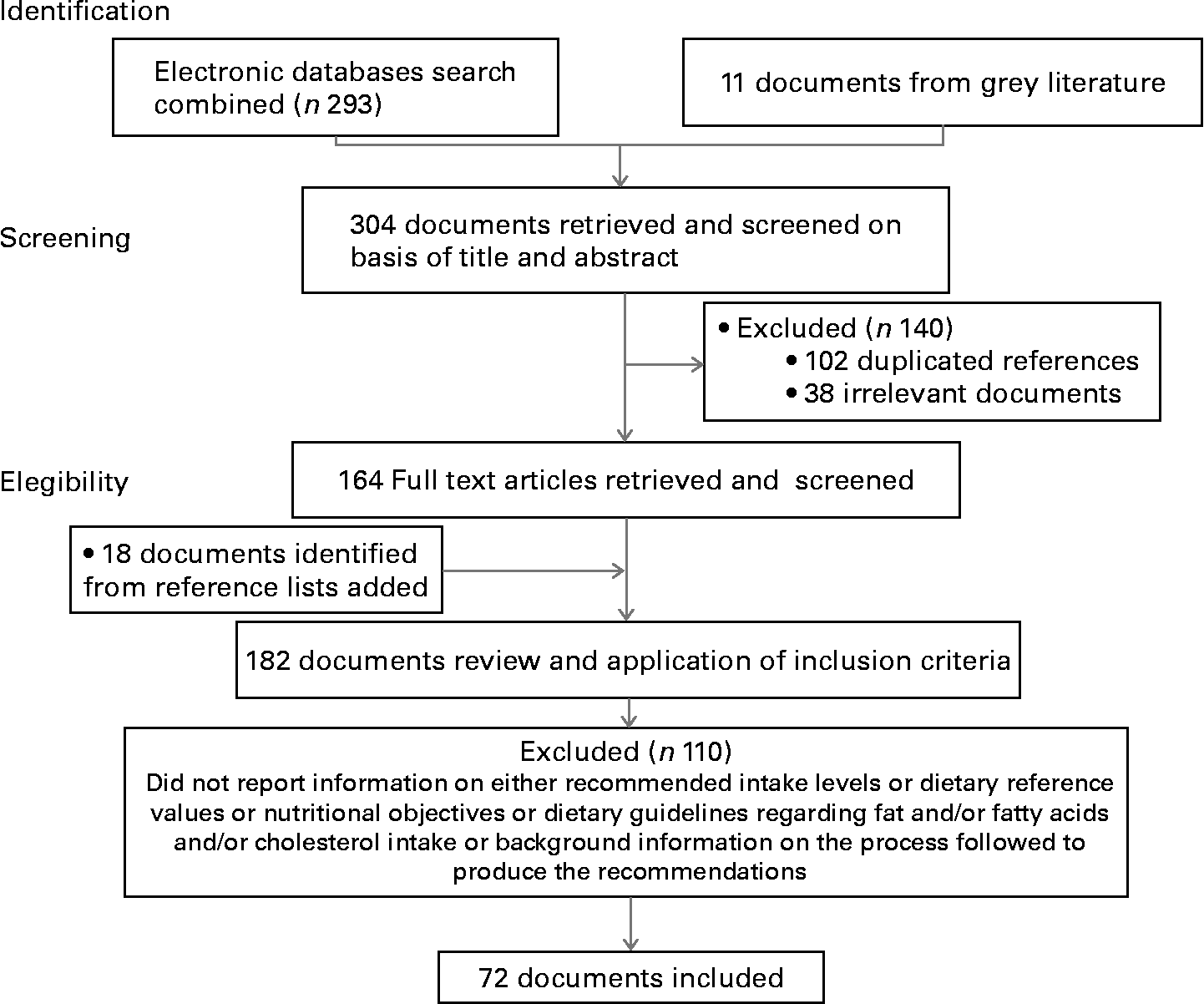



Recommended Dietary Reference Intakes Nutritional Goals And Dietary Guidelines For Fat And Fatty Acids A Systematic Review British Journal Of Nutrition Cambridge Core
· Normal hematocrit values are approximately 41% to 50% in males and 36% to 44% in females DRI is the general term for a set of reference values used for planning and assessing nutrient intakes of healthy people These values, which vary by age and gender, include Recommended Dietary Allowance (RDA) Average daily level of intake sufficient to meet theEU Dietary Reference Values Ketogenic 60/35/5 1800 Cal/Day Jean's Nutrient Profile 1 US government DRI, female 1930, Sedentary, NonLactating 1350 calories ketogenic jalva's US government DRI, male 1950, 1800calories Low Calorie, plus US government DRI, male 1950, 10 calories 3000calorie weightgain diet, 1 lb male (Domestic vs Imported – compares DRI values for a given food in domestically grown vs imported samples Impacts of the Food Quality Protection Act of 1996 ( FQPA ) – compares pre FQPA DRI values for a select group of major foods that were tested five or more times with values reported in 00, 04, and 11, quantifying the impact of this seminal legislation on pesticide dietary




4 General Guidance For Users Of Dris Session 3 The Development Of Dris 1994 04 Lessons Learned And New Challenges Workshop Summary The National Academies Press




Nutrition Tools Standards And Guidelines Ppt Download
DRI is the general term for a set of reference values used to plan and assess nutrient intakes of healthy people These values, which vary by age and sex, include Recommended Dietary Allowance (RDA) average daily level of intake sufficient to meet the nutrient requirements of nearly all (97%98%) healthy peopleAgricultural Business Remains Vital to Customers by Keeping Its OldFashioned Values Andy and Valerie Cole are the husband and wife team who own Andy's Agway in rural Dayton, Maine It's an impressive operation in no small part because the Coles still run their agricultural business on the fundamental values their family began with over a century ago Timothy P Hobbs, USDA RuralG Iron Intakes and Estimated Percentiles of the Distribution of Iron Requirements from the Continuing Survey of Food Intakes by Individuals (CSFII), 1994–1996, 474–484;



Plos One The Nutrient Balance Concept A New Quality Metric For Composite Meals And Diets




Guide To Good Food Nutrition And Food Preparation 14th Edition Page 148 162 Of 784
· The percentages of individuals meeting the Dietary Reference Intakes 1 (DRI) are based on day1 nutrient intakes from the CSFII and DRI values established during the period from the mid 1990's to 02 Pyramid Servings groups (fruit, grain, vegetable, dairy, and meat) estimates are for individuals 2 years old and over who meet the minimum daily servings recommendations · The percentages of individuals meeting the Dietary Reference Intakes 1 (DRI) are based on day1 nutrient intakes from the CSFII and DRI values established during the period from the mid 1990's to 02 Pyramid Servings groups (fruit, grain, vegetable, dairy, and meat) estimates are for individuals 2 years old and over who meet the minimum daily servings recommendations · USDA Recommended Sugar Intake Sugar lends delicious sweetness to food and gives an energy boost to your day when you're in a slump But Americans consume too much sugar, with 16 percent of the average diet coming from added sugars, according to the USDA's Dietary Guidelines for Americans 10 In fact, sugar is




Major Recommendations In Us Dietary Guidelines From 1980 To 15 Download Scientific Diagram




15e Ch02outline Lecture Notes Ch 2 Chapter Nutrition And Guidelines Chapter Nutrition And Guidelines Chapter Learning Objectives And Key Points State The Studocu
Chapter 1 describes these DRI values in detail Estimated Energy Requirements (EER), Recommended Dietary Allowances (RDA), and Adequate Intakes (AI) for Water, Energy, and the Energy Nutrients Age (yr) Reference BMI (kg/m 2) Reference Height cm (in) Reference Weight Protein kg (lb) Water a AI (L/day) Energy EER b (kcal/day) Carbohydrate Linolenic Acid RDA · For women age 3150 years, the AI is 1,500 mg of sodium per day The CDRR is "reduce intakes if above 2,300 mg/day" The committee didn't establish CDRR for potassium, although they lowered the potassium AIs The full charts for the new values can be found here Note that for sodium, we refer to the CDRR columnDRI values are listed by life stage group in Table 1 The Acceptable Macronutrient Distribution Range (AMDR) for protein is 5â percent of total calories for children 1 through 3 years of age, 10â 30 percent of total calories for children 4 to 18 years of age, and 10â 35 percent of total calories for adults older than 18 years of age For amino acids, isotopic tracer methods and linear




4 General Guidance For Users Of Dris Session 3 The Development Of Dris 1994 04 Lessons Learned And New Challenges Workshop Summary The National Academies Press




Dietary Guidelines For Americans




Chapter 2 Nutrition Tools Standards And Guidelines Nutrition Concepts Controversies 12e Sizer Whitney Slideshow And Powerpoint Viewer Learning Objectives Explain How Rda Ai Dv And
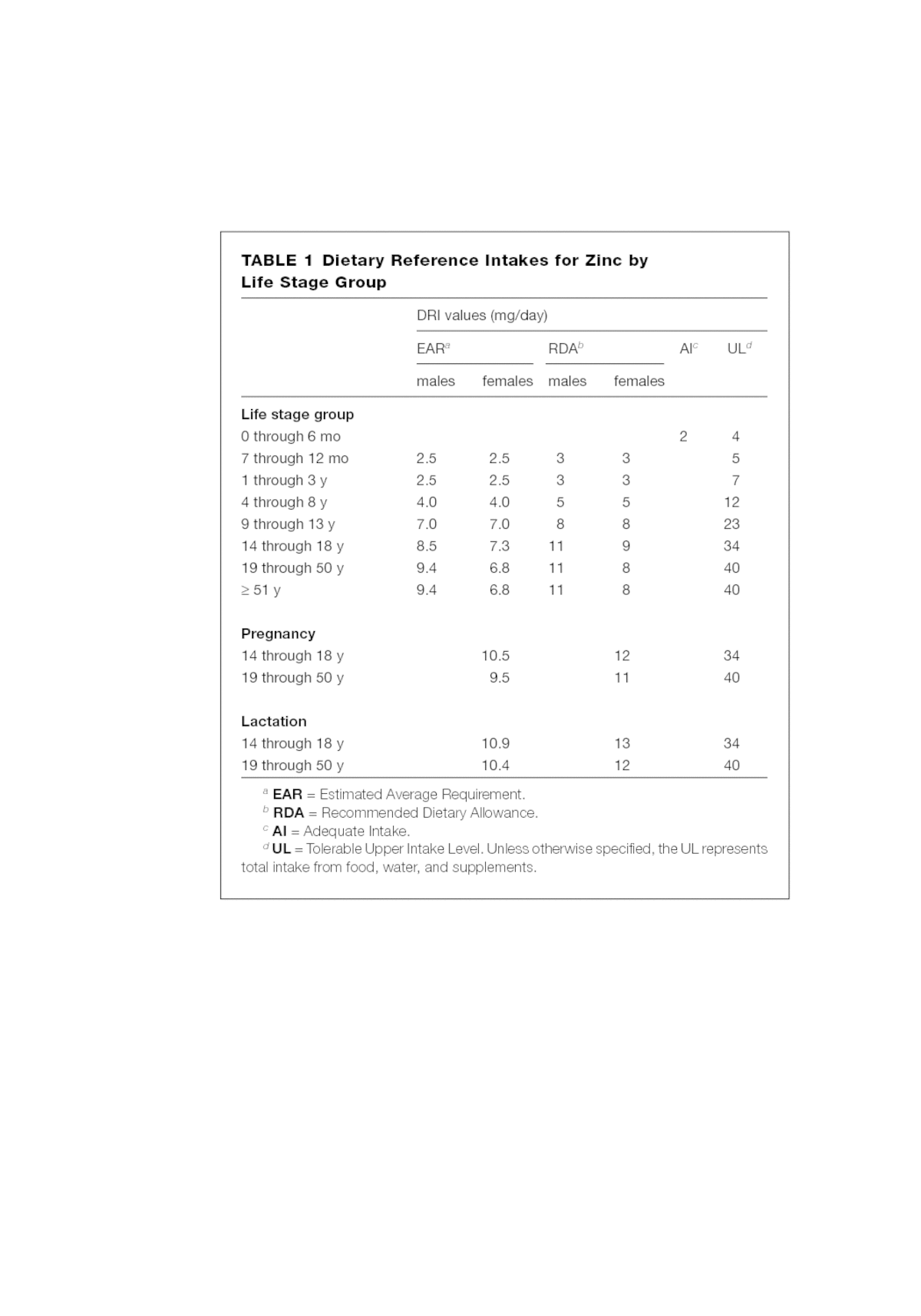



Zinc Dietary Reference Intakes The Essential Guide To Nutrient Requirements The National Academies Press




Pdf Reference Materials To Evaluate Measurement Systems For The Nutrient Composition Of Foods Results From Usda S National Food And Nutrient Analysis Program Nfnap




Practice Paper Of The American Dietetic Association Using The Dietary Reference Intakes Journal Of The American Dietetic Association




Federal Register Revision Of The Nutrition Facts Labels For Meat And Poultry Products And Updating Certain Reference Amounts Customarily Consumed




Pdf Dietary Reference Intakes Guiding Principles For Nutrition Labeling And Fortification Semantic Scholar




Nutrition Concepts And Controversies 14th Edition Sizer Test Bank By Haleskang Issuu




Human Nutrition Dietary And Nutrient Recommendations Britannica




Chapter Two Dietary Standards




Building A Better Nutrient Density Index Optimising Nutrition




Dietary Intakes Of Women S Health Initiative Long Life Study Participants Falls Short Of The Dietary Reference Intakes Journal Of The Academy Of Nutrition And Dietetics




4 General Guidance For Users Of Dris Session 3 The Development Of Dris 1994 04 Lessons Learned And New Challenges Workshop Summary The National Academies Press




Options For Basing Dietary Reference Intakes Dris On Chronic Disease Endpoints Report From A Joint Us Canadian Sponsored Working Group Abstract Europe Pmc
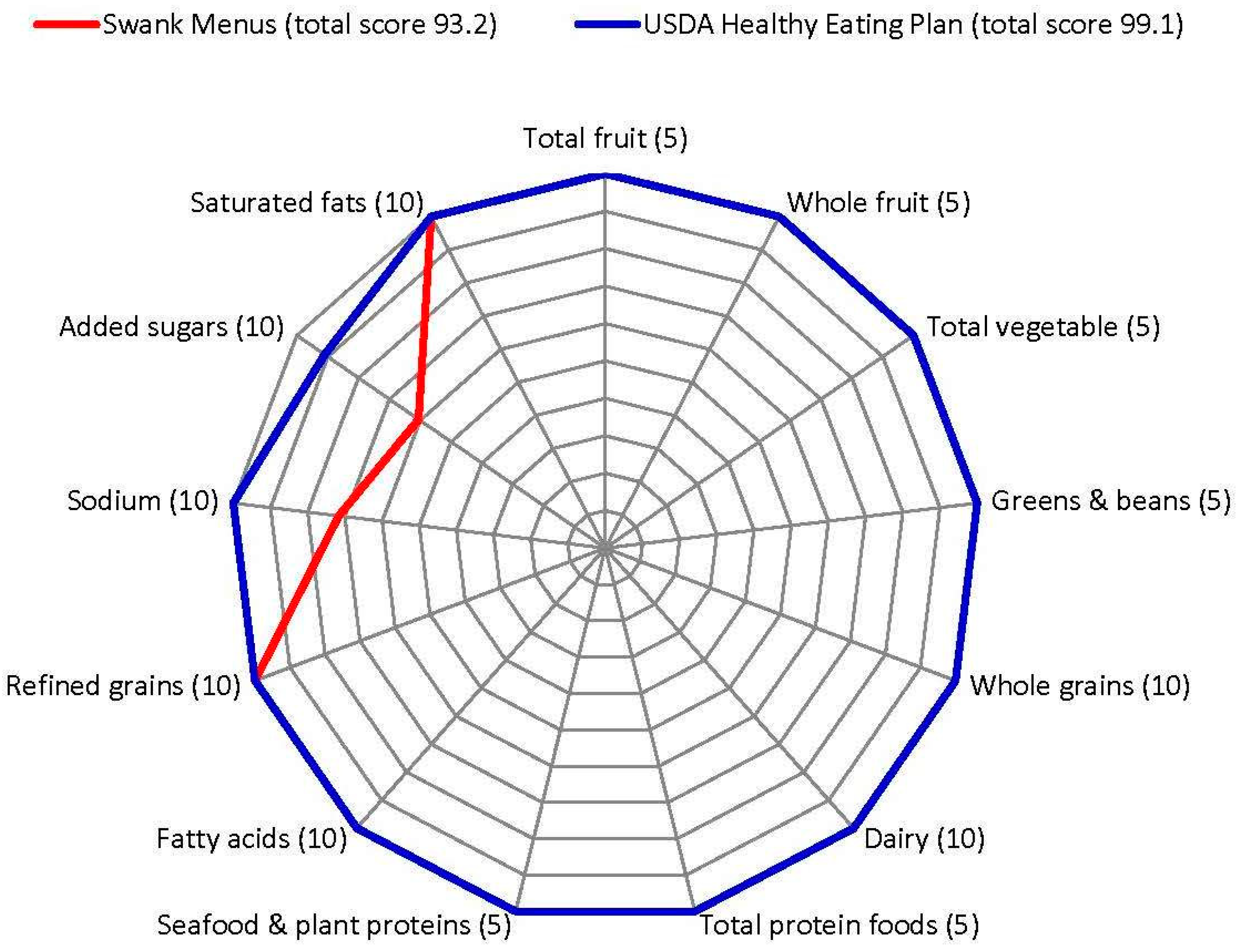



Nutrients Free Full Text Nutrient Composition Comparison Between The Low Saturated Fat Swank Diet For Multiple Sclerosis And Healthy U S Style Eating Pattern Html




What Is The Difference Between Dri Daily Value




Choosing Foods Wisely Chapter Ppt Download




Nutrients Free Full Text Personalized Nutrient Profiling Of Food Patterns Nestle S Nutrition Algorithm Applied To Dietary Intakes From Nhanes Html



Dietary Fiber Ingredients Expanding Options For Meeting Dietary Fiber Recommendations Is A Selfstudy Module Produced By The Calorie Control Council Pdf Free Download




Pdf Dietary Reference Intake Dri Value For Dietary Polyphenols Are We Heading In The Right Direction
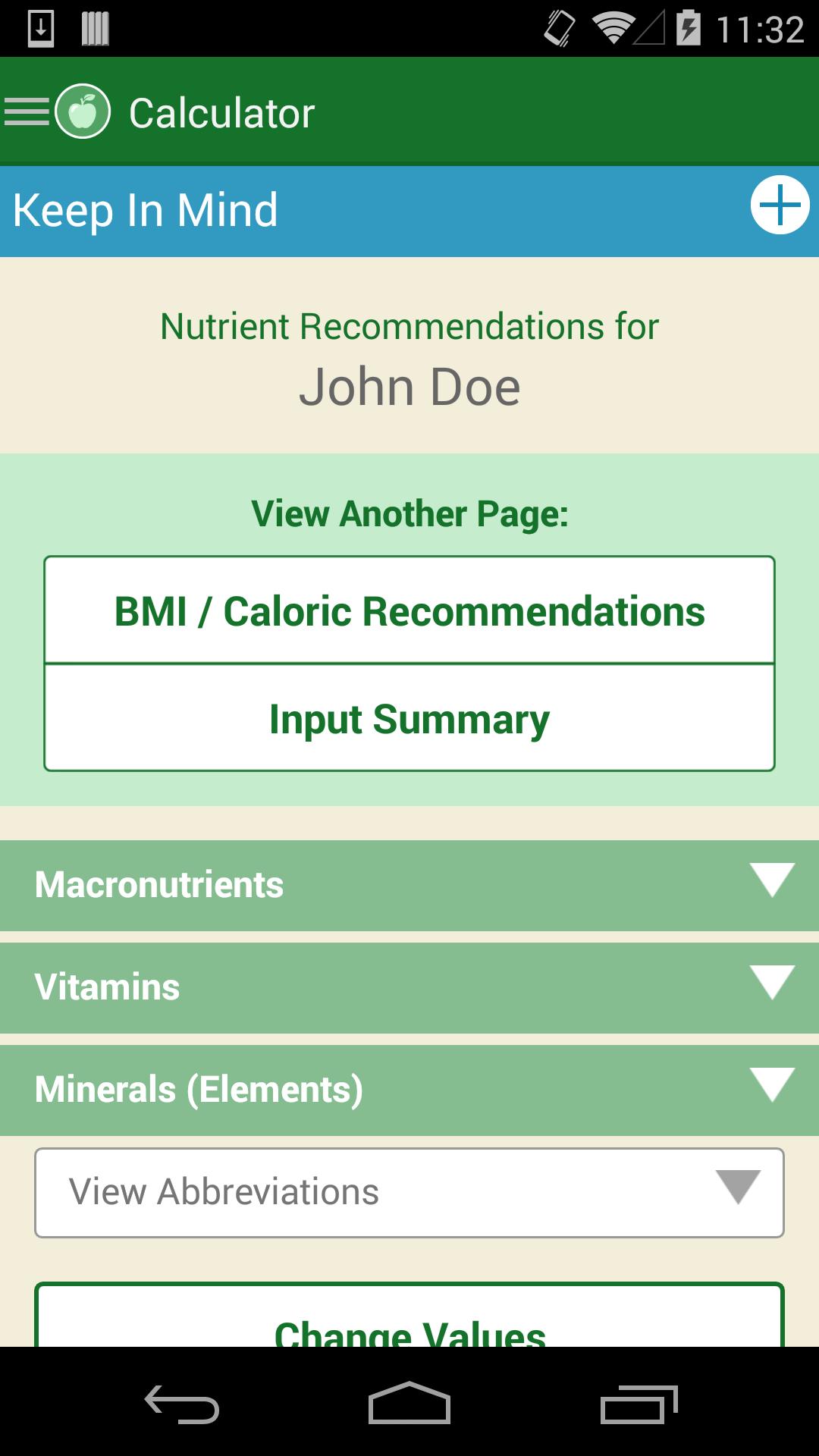



Usda Dri For Android Apk Download




Ppt Chapter 2 Nutrition Tools Standards And Guidelines Powerpoint Presentation Id
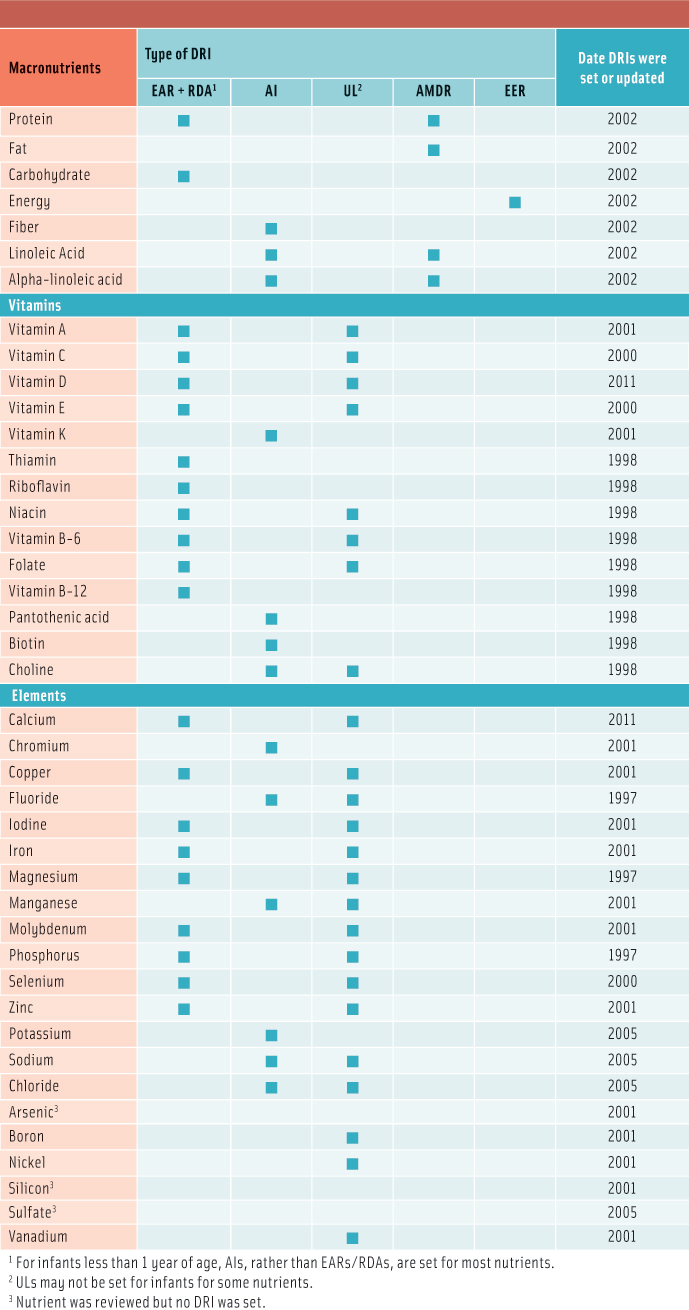



Food Scientists Dietary Reference Intakes An Important Alliance Ift Org




Dapa Measurement Toolkit




What Are The Daily Nutritional Requirements For Adults
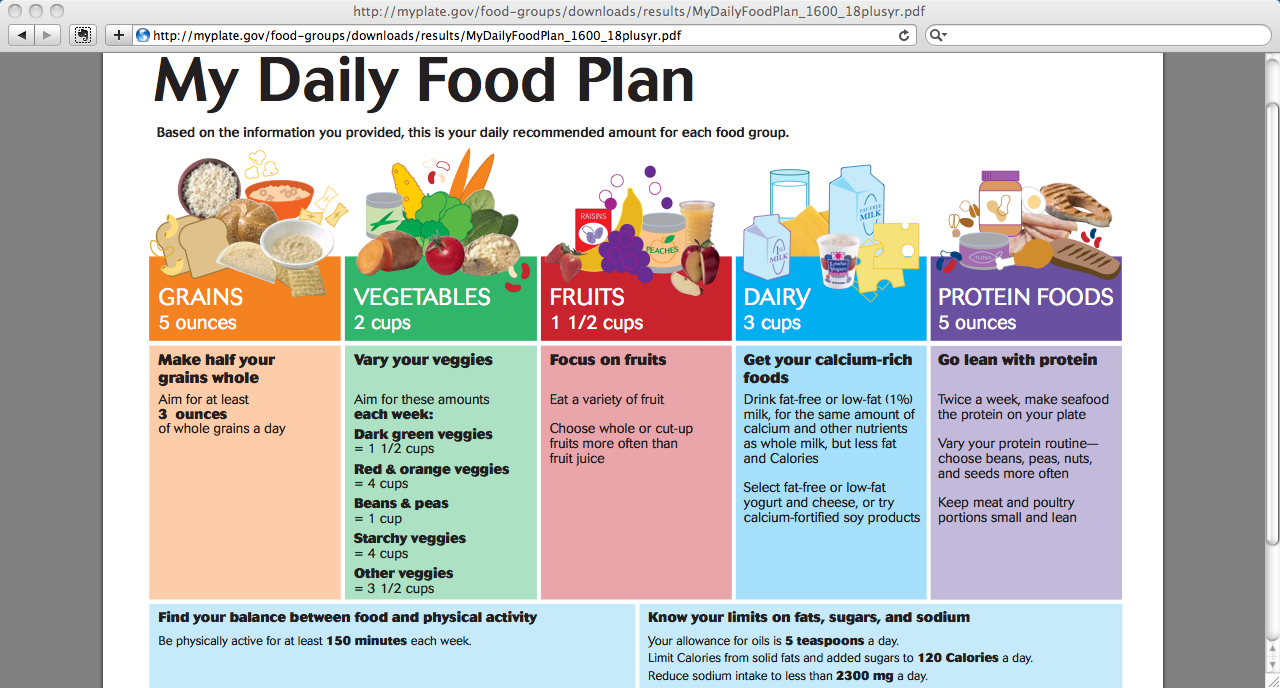



Lecture 2a Chapter 2




Chapter 2 Nutrition Tools Standards And Guidelines Studocu




Ppt 05 Dietary Guidelines For Americans And The New Dietary Reference Intakes Potential Implications For The Nslp And Powerpoint Presentation Id




Chapter 2 Nutrition Tools Standards And Guidelines Nutrition Concepts Controversies 12e Sizer Whitney Slideshow And Powerpoint Viewer Learning Objectives Explain How Rda Ai Dv And




Guide To Good Food Nutrition And Food Preparation 15e Textbook Page 137 151 Of 784




Recommended Dietary Intakes Nutritional Doublethink




Usda Dri For Android Apk Download




Chapter 2 Nutrition Tools Standards And Guidelines Nutrition Concepts Controversies 12e Sizer Whitney Slideshow And Powerpoint Viewer Learning Objectives Explain How Rda Ai Dv And




Dapa Measurement Toolkit




5 Nutrition Your Health Today 6th Edition Ppt Download
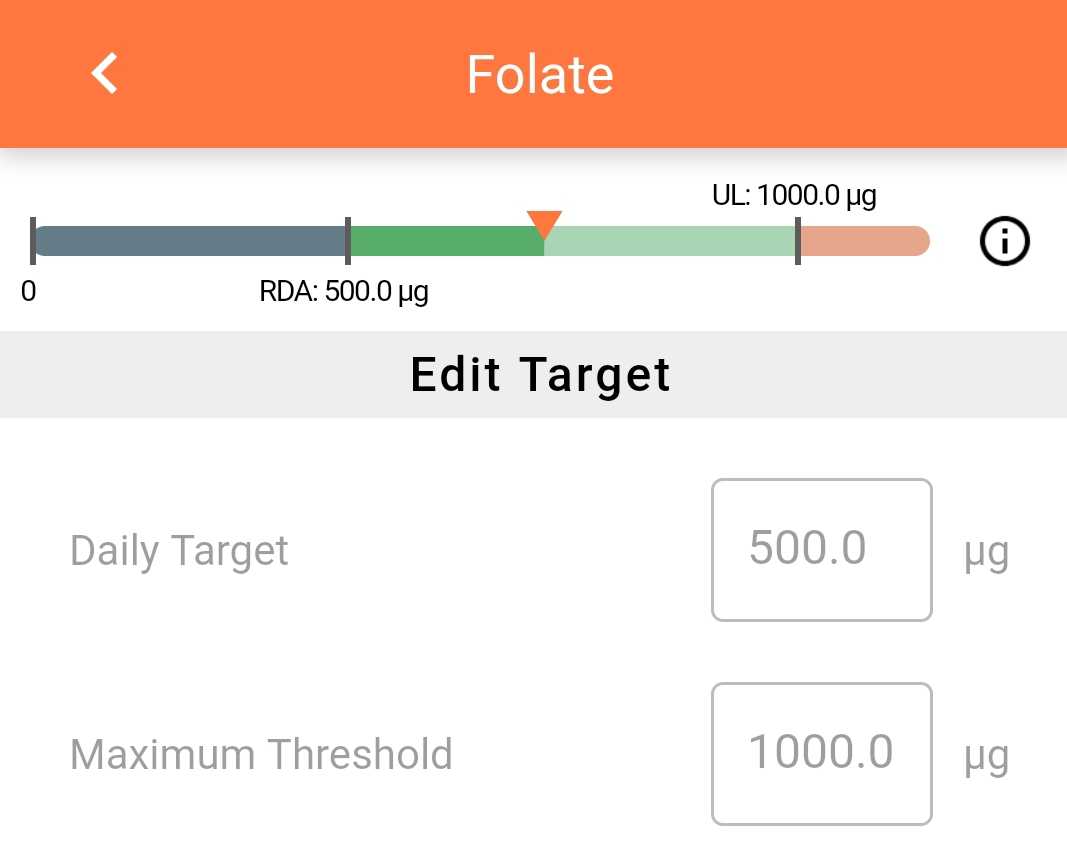



Dietary Reference Intakes Dris Cronometer




Pdf The Usda Food And Nutrient Database For Dietary Studies 5 0




Guide To Good Food Nutrition And Food Preparation 14th Edition Page 147 161 Of 784
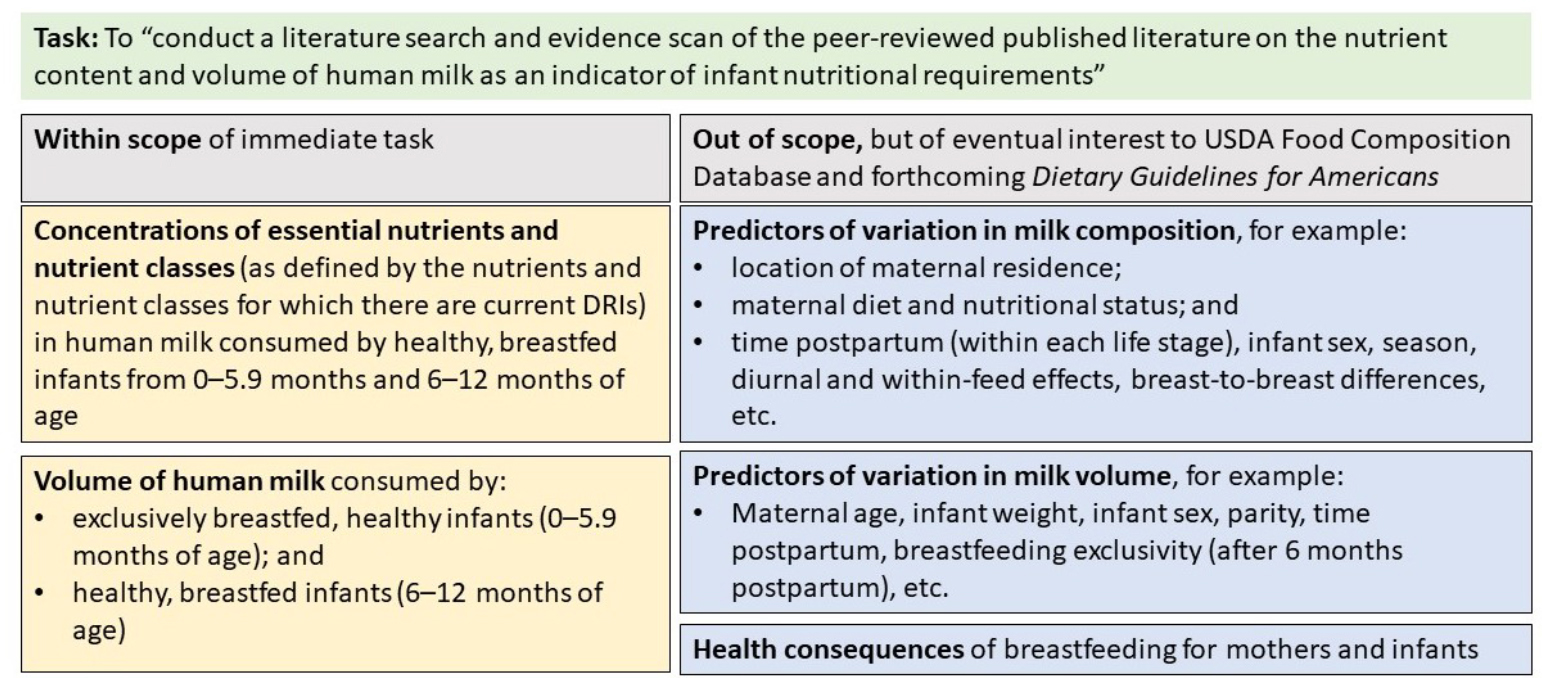



1 Introduction Scanning For New Evidence On The Nutrient Content Of Human Milk A Process Model For Determining Age Specific Nutrient Requirements The National Academies Press




Chapter 3 Nutrition Needs Of Adolescents


